ACERCA DE LEED
Desarrollada por el U.S. Green Building Council
LEED is a working system to identify, implement and measure the design, construction, operations and maintenance of sustainable architecture projects, from buildings to colonies.
LEED is a consensual tool in constant relationship with the sustainable construction market that is adopted on a voluntary basis and that serves as a guide and advisory mechanism during the construction process. LEED certification systems are targeted at commercial, institutional, residential, and neighborhood and community developments.
The objective of LEED is to optimize the use of natural resources, promote regenerative strategies, maximize the positive impacts and minimize the negative impacts of construction activities on the environment and on human health, and promote high-quality interior spaces for the occupants of the buildings. . LEED promotes inclusive design, the incorporation of existing technology and the most advanced sustainability strategies to promote knowledge in sustainable construction and transform its associated practices. LEED seeks a balance between regulatory compliance and the development and implementation of innovative strategies. LEED nevertheless defines a set of affordable benchmarks that define the baselines for defining sustainable interior spaces, buildings and neighborhoods.
LEED for New Construction and Major Renovations was first developed in 1998 for the commercial building industry (primarily offices) and has since been updated numerous times. Since its launch, LEED has evolved to serve and serve new markets and building types, advances in technology and construction practice, and to better understand the effects of the built environment on the health of people and our environment.
These ongoing enhancements, developed by USGBC committee and subcommittee volunteers in conjunction with USGBC staff, have been reviewed by the LEED Steering Committee and the USGBC Board of Directors before being sent to USGBC members for voting. The process is based on principles of transparency, openness and inclusiveness.
LEED GOALS
LEED assessment systems aim to promote the transformation of the construction industry through strategies that pursue the following objectives:
Reverse the contribution to climate change.
Improve human health and well-being.
Protect and restore water resources.
Protect, improve and restore ecosystem services and their biodiversity.
Promote sustainable and regenerative material cycles.
Contribute to building a circular economy.
Improve social balance, environmental justice, community health and quality of life.
These objectives are the basis for LEED credits and prerequisites. In the BD + C certification system, credits are categorized as Location and Transportation (LT), Sustainable Sites (SS), Water Efficiency (WE), Energy and Atmosphere (EA), Materials and Resources (MR), and Indoor Environmental Quality (EQ).
The objectives also weigh the points in the process towards certification. Each credit in the certification system is ranked according to the relative importance of its contribution to the objectives of each area. The result is a weighted average: credits that address the most important objectives receive the highest weights. Project teams that meet project prerequisites and earn enough credits demonstrate project performance in an integrated and cross-cutting way.
LEED BENEFITS
LEED is designed to meet the challenges faced by the construction industry while responding to the needs of an increasingly competitive market. The LEED Reference Guide for New Construction Projects gives homeowners and developers, as well as project managers and other project teams, the tools they need to both improve building operations and improve the quality and environmental health of buildings. Interior spaces.
LEED certified buildings are designed to provide the following benefits:
Reduced operating costs and increased property value.
Reduction of waste sent to landfill (both in the construction phase and in the operational phase).
Water and energy conservation strategies.
Healthier and more productive spaces for occupants.
Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
CORPORATE VALUE
The aforementioned aspects affect the operation and occupation phase of a building. From the point of view of a public-private developer, we can consider the following benefits:
LEEDTM Value: The project will be certified following an internationally recognized and verified methodology that guarantees that the architectural design, facilities and construction follow strict sustainability parameters, so that the impact on the environment and natural resources is minimized throughout the life cycle of the building.
Reinforcement of the corporate image and environmental commitment: Obtaining the LEED environmental certification is the best way to show society, and especially the users of the building, the environmental commitment of the building and of the people.
Sustainability positioning: Being an example of a building with high environmental quality, with the benefit of social recognition and publicity.
Higher profitability: Higher market value (sale or rent) and reduction of revisions and maintenance in the operational phase. Cost benefit: Analysis of the real cost of the sustainability strategies to be implemented in the project and agreement by conducting an “eco-charrette” with all project teams.
LEED BUILDING DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION
LEED BUILDING DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION
The classification system considered for the budgeted project will be LEED BD + C (Building Design and Construction) version 4, which includes:
New Construction and Major Renovations: Directs design and construction activities for both new construction and major renovations of existing buildings. This includes major improvements to HVAC systems, significant modifications to the building envelope, and major interior renovations.
Core and Shell: For projects where the developer fully controls the mechanical, plumbing and electrical systems, the HVAC systems and the firefighting systems (Core) and the envelope (Shell), but not the final version of the design and construction for the lessee.
Schools: For buildings composed of the core and complementary learning spaces in the primary and secondary grades. It can also be used in higher education buildings and non-academic buildings within an educational campus.
Retail: Addresses the unique needs of retailers - banks, restaurants, clothing stores, department stores, etc.
Data Centers: For buildings specifically designed and equipped to meet the needs of high-capacity computing equipment such as servers, used for data storage and processing.
Warehouses and Distribution Centers: For buildings used to store merchandise, manufactured products, articles, raw materials, or personal belongings, such as self-storage warehouses.
Hospitality: Dedicated to hotels, motels, hostels, or other businesses within the service industry that provide temporary or transit accommodation, with or without food.
Healthcare: For hospitals that operate twenty-four hours a day, seven days a week and provide medical treatment to patients, including intensive and / or long-term care.
THE LEED CERTIFICATION PROCESS The LEED certification process begins when the project team selects the most appropriate certification system and registers the project. From this moment on, the project is designed to meet all the prerequisites of the different fields and those credits for which it has been agreed to opt for the “eco-charrette” sessions. LEED has four levels of certification depending on the points achieved: Certified, 40–49 points Silver, 50–59 points Gold, 60–79 points Platinum, 80+ points

METHODOLOGY
The certification system for this project is LEED v4 New Construction. This system evaluates project performance in the following areas:
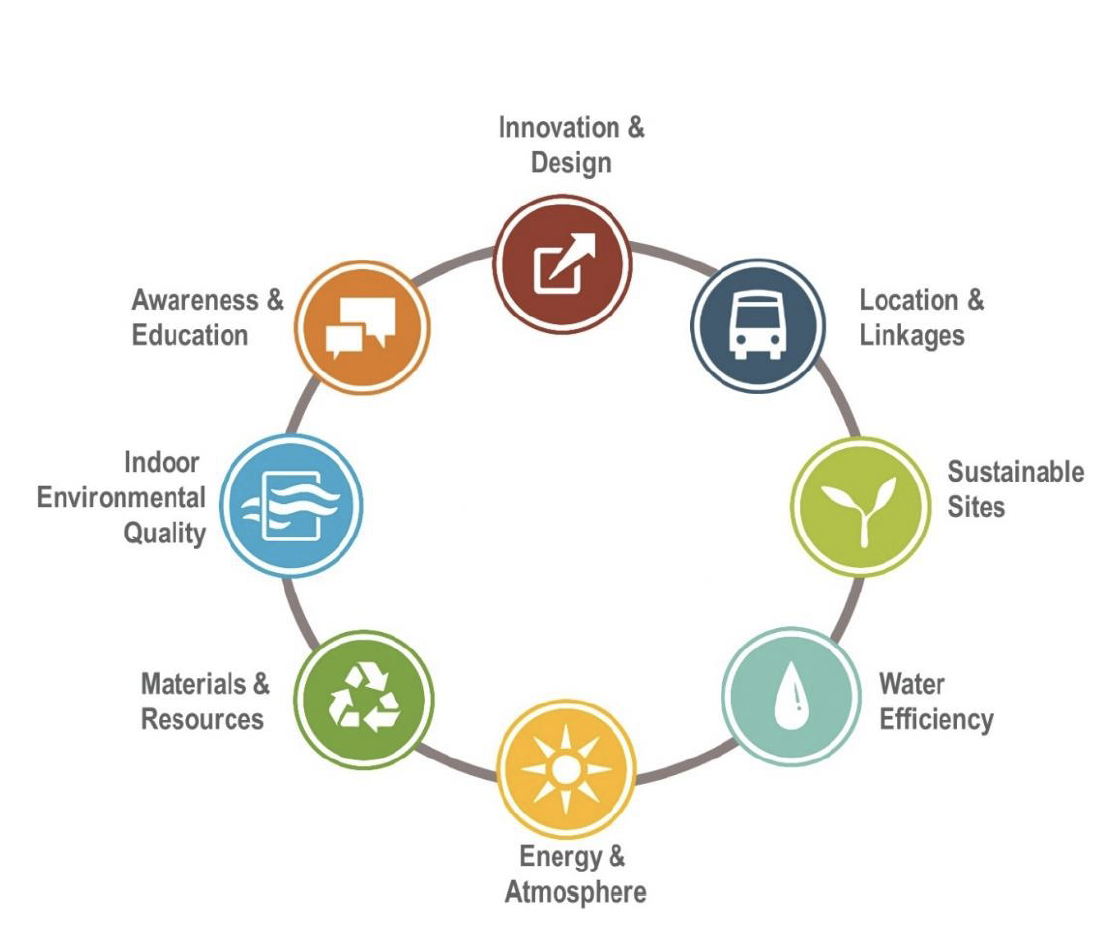
LOCATION AND TRANSPORTATION: evaluation of decisions about the location of the project, connectivity and access to services.
SUSTAINABLE SITES: analysis of the environment of the project plot and of the interconnections between the different elements and their biodiversity.
WATER EFFICIENCY: efficiency in the use of water and in reuse strategies.
ENERGY AND ATMOSPHERE: energy efficiency, incorporation of renewable facilities in the project, purchase of green electricity.
MATERIALS AND RESOURCES: use of regional materials, recycled and recyclable materials as well as the reuse of existing structures and materials in the project.
INTERIOR ENVIRONMENTAL QUALITY: through the design and incorporation of specific materials to guarantee the interior environmental quality of the project to promote the well-being and productivity of its occupants.
INNOVATION: incorporation into the project of innovative strategies (saving water and / or energy, certified materials "Cradle to Cradle", etc.) or for achieving performances superior to those required in certain credits.
REGIONAL PRIORITY: being a project outside the United States, this area does not apply to the project.




